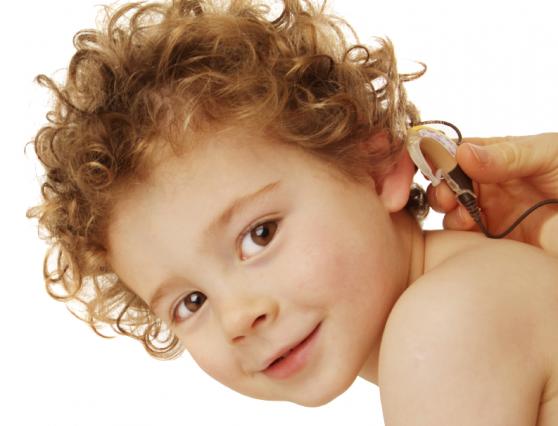
A cochlear implant (CI) is a hearing aid that requires surgery. It’s meant for people who are deaf or suffer from severe and very severe hearing loss, and for whom the amplification provided by a traditional hearing aid isn’t sufficient. A cochlear implant doesn’t provide its user with a normal hearing, but it makes learning to speak via hearing possible.
A cochlear implant system consists of an internal part, i.e. theimplant, and an external part, i.e. the speech processor. The cochlear implant converts sound into coded electric impuksese. These impulses are conveyed into the auditory nerve and the brain interprets them as sound.
Cochlear implants were first used in the early 1980s in England. In Finland, children have been implanted since 1997. In the beginning children were implanted in one ear and since 2010 receiving a bilateral implant has been an option nationwide. At the moment cochlear implants are used as rehabilitation for children born with a severe enough degree of hearing loss that the amplification provided a hearing iaid is insufficient.




